Autoimmune skin diseases
Your autoimmune skin disease may affect you in a different way, which means your treatment has to be specially formulated to work for you alone. Autoimmune conditions occur when your immune system mistakenly attacks your body. This may sound very scary, but the conditions vary from person to person. The cause is usually unknown, but there are treatments to manage most autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune skin diseases can manifest in different ways. Whatever you symptoms are, your dermatologist will give you an accurate diagnosis. Dr Ayanda Motau is experienced in dealing with these conditions, you will have the opportunity to conversate and learn more about your skin condition during your visit and how you can prevent it from disturbing your daily life.
Types of autoimmune skin diseases
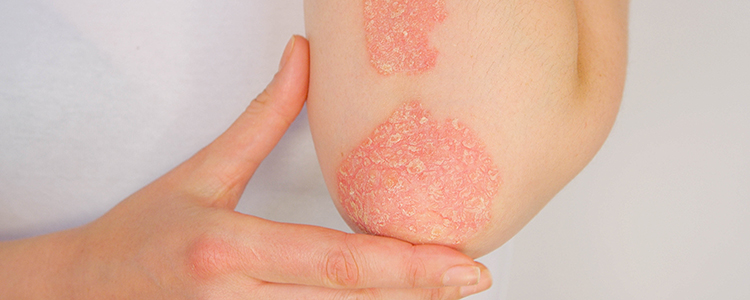
Psoriasis: Inflammatory skin condition resulting from overactive skin cells.
Alopecia areata: Hair loss creating large bald spots. Your immune system attacks your hair follicles.
Scleroderma: This disease results in patches of thickened skin which comes in two ways; systemic sclerosis (SS) and CREST syndrome.
Dermatomyositis: Primarily muscular in nature, but affects the skin as well. It is distinguished by skin rash thickening and tightening of the skin in many areas.
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: It is difficult to diagnose but normally occurs after the age of 50 years. It causes fluid-filled skin blisters.
Causes
No direct cause has been linked to autoimmune skin disease. Nevertheless, there are people who are more likely to get the disease because they carry the gene. Whether you developed your condition as an infant or later on in life, your life should not change drastically. You can still enjoy daily activities and functions. It is important to know what triggers your condition and how you can combat that.
Common autoimmune skin disease triggers:
- Hormones.
- Infections.
- UV rays from the sun.
- Pesticides.
- Some medications